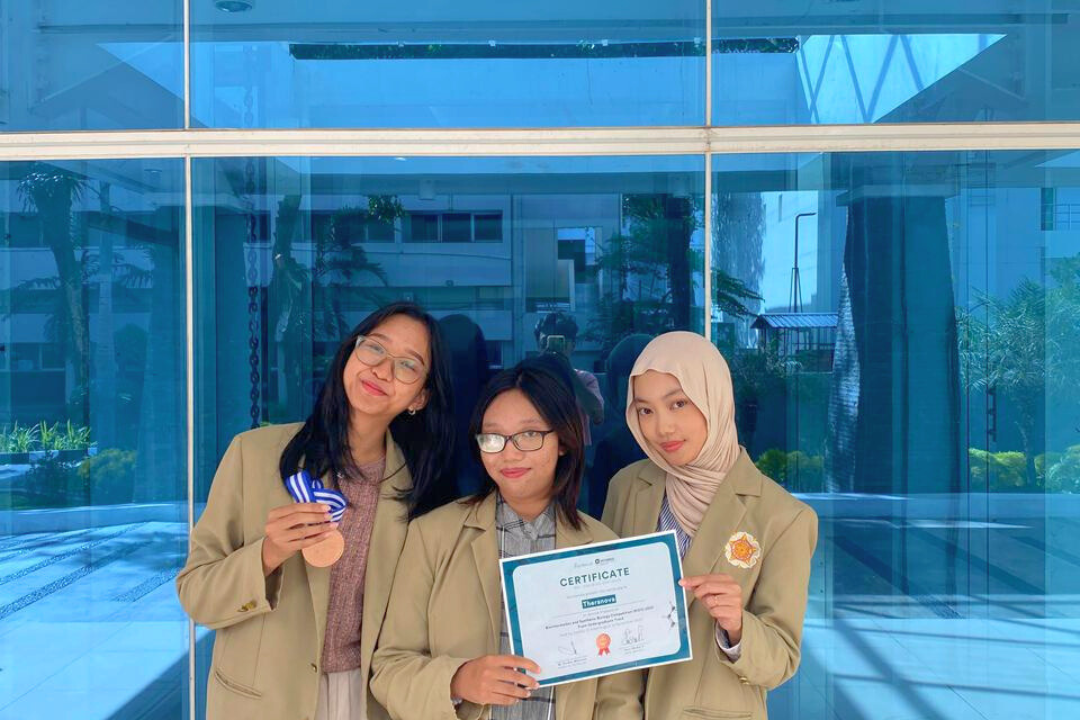
Students from the Faculty of Pharmacy at Gadjah Mada University (UGM) have once again made their mark on the international stage by winning a bronze medal at the Bioinformatics and Synthetic Biology Competition. The Faculty of Pharmacy at UGM, represented by Team “Theranova,” participated in the competition organized by synbio.id, a non-profit organization focused on accelerating the fields of synthetic biology and bioinformatics.
The Theranova team is a collaboration between universities consisting of students from Gadjah Mada University, University of Indonesia, Brawijaya University, Andalas University, and Universiti Malaya. The Faculty of Pharmacy at UGM is represented by three students from the class of 2023, namely Gresmawarrenes Jamus, Khansa Nismara Firdauza, Sekar Ayu Larasati, and Icha Dwi Anggita.
Under the guidance of UGM Faculty of Pharmacy lecturer Prof. Dr.rer.nat. apt. Adam Hermawan, M.Sc., the team presented in-depth research entitled “Engineering Chimeric Lipid Nanolipids Functionalized with Di-Rhamnolipids for Selective Delivery of PGV-1 to Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.” The research focused on optimizing drug delivery systems through the design and modeling of Chimeric Lipid Nanolipids. The use of di-Rhamnolipid biosurfactants was key in ensuring that the small PGV-1 molecules could be selectively delivered as a precise anticancer agent to Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) cells.
The competition took place through a series of rigorous selections from August to November 2025. The stages began with the collection of abstracts, the development of a project showcase website, and the fulfillment of output targets. In the final stage, the Theranova Team presented their innovative ideas to the jury and won a bronze medal for the excellence of their concept and methodology.
This achievement is a tangible manifestation of academics’ contribution to supporting global sustainable development goals or Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) number 3, namely Good Health and Well-being, number 4, namely Quality Education, and number 17, concerning partnerships to achieve goals. Through innovations in TNBC treatment, this research aims to provide more effective and safer therapeutic solutions for breast cancer patients, while also contributing to reducing mortality rates from non-communicable diseases through advancements in pharmaceutical technology (SDG No. 3).
This success reflects the quality of higher education that is capable of integrating research and innovation. Through this competition, students not only master theory, but also practice advanced bioinformatics and molecular biology skills (SDG no. 4). Additionally, the cross-institutional collaboration between UGM, UI, UB, UNAND, and Universiti Malaya, as well as the synergy between faculty advisors and students, highlights the importance of strategic partnerships in addressing complex global health challenges (SDG 17).